Guidelines for Secure IT Asset Disposal

Having a hardware decommissioning process in place is a practice that’s too often forgotten by IT departments. Unfortunately, this has created an ongoing issue of devices that contain corporate data, such as routers and printers, being sold on the secondhand market.
The problem of failing to decommission hardware was recently highlighted by a research team for ESET when they purchased 18 used routers for test purposes. The team was shocked to discover data on 56% of the devices, including customer information, router-to-router authentication keys and application lists. If this data fell into the wrong hands, it would have been enough to launch a cyberattack.
Now that organizations own more hardware and IoT devices than ever, there’s more potential security and compliance issues they can run into by failing to decommission old equipment. In this blog, we will share a 5-step secure disposal checklist for anyone that’s tasked with ensuring data protection within an organization.
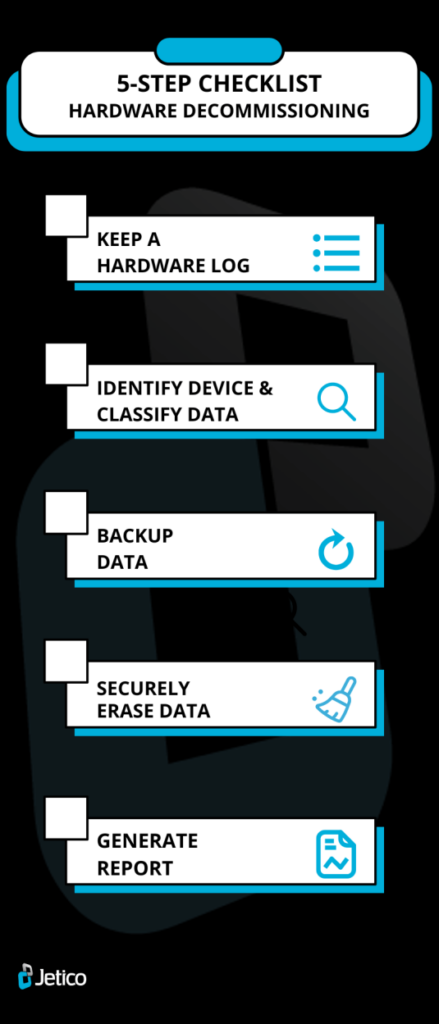
5-Step Checklist for Hardware Decommissioning Process
The lesson that should be taken from the ESET research is that any device leaving your company must be sanitized in order to ensure organizational secrets are not being openly sold in secondhand hardware markets.
Although organizations should create their own set of guidelines that IT teams can follow to decommission or securely dispose of old devices, we have listed 5 steps that should at least be considered for inclusion in such a document.
Step 1: Stay Organized by Keeping a Hardware Log
By creating and managing a hardware log, your organization will be able to keep track of all the hardware that’s been decommissioned. The log can be used to record relevant information relating to your retired hardware, such as the ID name or number, the date of decommission and the disposal partner (ITAD) that may have assisted in wiping the device. Having this information at hand will not only help you to stay organized, but it may be useful for compliance reasons too.
Step 2: Identify Device & Classify Information
Firstly, you need to understand what type of hardware you’re working with. Each device has its own particular needs, so the best method of removing data from a given piece of hardware will differ accordingly.
Next, you will want to establish what kind of data is stored on the hardware in question. Ask yourself what services the device ran and who were the main users of the hardware. If you come to the conclusion that the data is sensitive or in any way identifiable, you should actively take steps to remove it before it leaves your organization.
Step 3: Backup Your Data
Even if you have processes in place for automatically backing up hardware within your data center, you should safeguard against failure by creating a backup copy of the information a device holds before decommissioning it. Backup data can be important for keeping hold of proprietary information or any important configurations that may be needed going forwards. In addition, backups might be needed for legal reasons to provide proof of the data that a particular device stored before disposal.
Step 4: Securely Erase Data
Resetting the hardware can sometimes be enough to make data disappear for good. If it’s a router, you will want to consult the relevant manufacturer’s guidelines to find out how to restore the device to its factory settings.
For PCs, MacBooks, mobile phones, USB sticks and most other devices, restoring to factory settings won’t be enough to permanently remove the stored information. In these cases, you should use enterprise-level data sanitization software, such as BCWipe Total WipeOut, to securely erase all existing data from the device in question. If your organization is not confident about doing this in-house, you should work with a trusted disposal partner that can wipe the data for you and verify that it’s disappeared for good.
It’s never recommended to remove data from a device by destroying it. Resorting to physical destruction doesn’t guarantee that your data can’t be restored by a third party, while it also creates harmful electronic waste and rules out the prospect of the device in question being reused.
Step 5: Generate Report for Compliance
Once the hardware has been decommissioned, you may want to generate a report that provides proof of effective deletion. This is often needed for compliance reasons, so make sure you purchase sanitization software that provides this kind of feature or work with disposal partners that offer this service.
Learn More about Data Wiping for Your Hardware Decommissioning Process
Now you know about the importance of decommissioning hardware and have read through our 5-step checklist, your organization’s corporate secrets should never be anywhere near the secondhand tech market. To read more about the importance of data sanitization, why not check our ultimate guide to securely wiping computer hard drives clean?
Happy Wiping!
Related Articles
Data Sanitization 5 Common Myths
The Ultimate Guide to Deleting Files Permanently
CMMC 2.0 Levels, Controls & Framework for Media Sanitization Requirements
NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization Explained
IEEE 2883-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage
IRS Publication 4812 & How to Comply with Wiping Standards
How to Securely Wipe Your Windows 11 Computer Clean
How to Wipe a Hard Drive on a Dead Computer
How to Wipe an NVMe Drive
How to Delete Files on SSD
