
CMMC 2.0 compliance is a necessity for all organizations and entities that wish to secure contracts with the United States Department of Defense (DoD).
A framework that sets the standard for data security practices within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB), CMMC 2.0 is an update to the first version of the certification that was released in 2021.
In this blog, you can find an overview of CMMC 2.0 and answers to the most important questions regarding the regulation. We will then summarize the CMMC 2.0 levels, controls and overall framework, before outlining the relevant media sanitization requirements and explaining how your organization can successfully comply with the certification.
What Does CMMC Stand For?
CMMC is short for Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification. The original version of the certification, CMMC 1.0, was issued by the DoD in 2020 to improve cybersecurity practices across the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). A new and simplified version of the standard was then launched in November 2021 as CMMC 2.0, which includes numerous updates to further help contractors in the DIB safeguard sensitive information.

Following recent concerns related to leaked US federal agency documents, there is speculation that CMMC 3.0 will be launched in the near future.
Who Needs CMMC Certification?
CMMC compliance is required for any organization or entity that wants to compete for DoD contracts. This includes primary contractors that work directly with the DoD, as well as subcontractors, suppliers and vendors. CMMC certification ensures that approximately 300,000 contractors in the Defense Industrial Base have robust cybersecurity measures in place to keep sensitive data protected.
When Will CMMC 2.0 Be Required for DoD Contracts?
According to the website for the DoD Chief Information Officer, “the changes reflected in CMMC 2.0 will be implemented through the rulemaking process” and “companies will be required to comply once the forthcoming rules go into effect.” It’s currently estimated that CMMC 2.0 will become law in 2024, but requirements based on the updated certification may have already begun appearing in DoD contracts. Therefore, it’s crucial that organizations within the DIB start demonstrating compliance with CMMC 2.0 in order to continue working with the DoD.
CMMC 2.0 Model & Changes to the CMMC Framework
Compared to the CMMC 1.0 model with its 171 security practices spread across 5 levels, the newer version of the certification provides organizations with a more simplified framework. Not only has the CMMC 2.0 been streamlined down to 3 compliance levels, but it now aligns with the widely accepted National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cybersecurity standards. In addition, all CMMC unique practices and maturity processes have been eliminated.
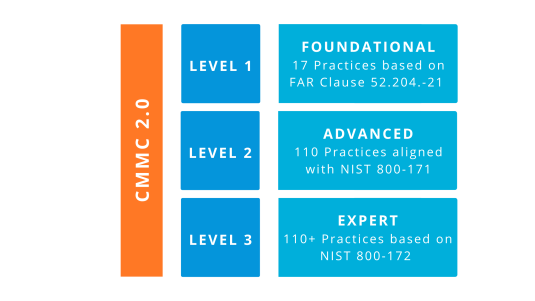
CMMC 2.0 Levels
Let’s take a closer look at the 3 levels of the CMMC 2.0 framework:
- CMMC 2.0 Level 1
Described as “Foundational”, the first level is for organizations that handle or process Federal Contract Information (FCI) only. This type of information is not intended for public release and requires protection, but it’s not critical to national security. Level 1 contains a total of 17 security practices and it requires organizations to carry out annual self-assessments. - CMMC 2.0 Level 2
The “Advanced” level, this middle tier is for organizations that handle or process Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Level 2 contains 110 security practices, all of which are aligned with NIST SP 800-171. To comply with this level, organizations must receive third-party assessments for prioritized acquisitions, or carry out self-assessments for non-prioritized acquisitions. - CMMC 2.0 Level 3
The last tier is the “Expert” level, which is only for organizations that handle or process the highest priority programs with CUI. Level 3 contains over 110 security practices and its requirements are aligned with a subset of NIST SP 800-172. For organizations, this level will be assessed by government officials.
CMMC 2.0 Media Sanitization Requirements
Now you have a better understanding of the CMMC 2.0 levels, it would be helpful to know how to comply with the certification’s media sanitization requirements. Here’s what the controls in each level have to say about sanitizing media and data wiping:
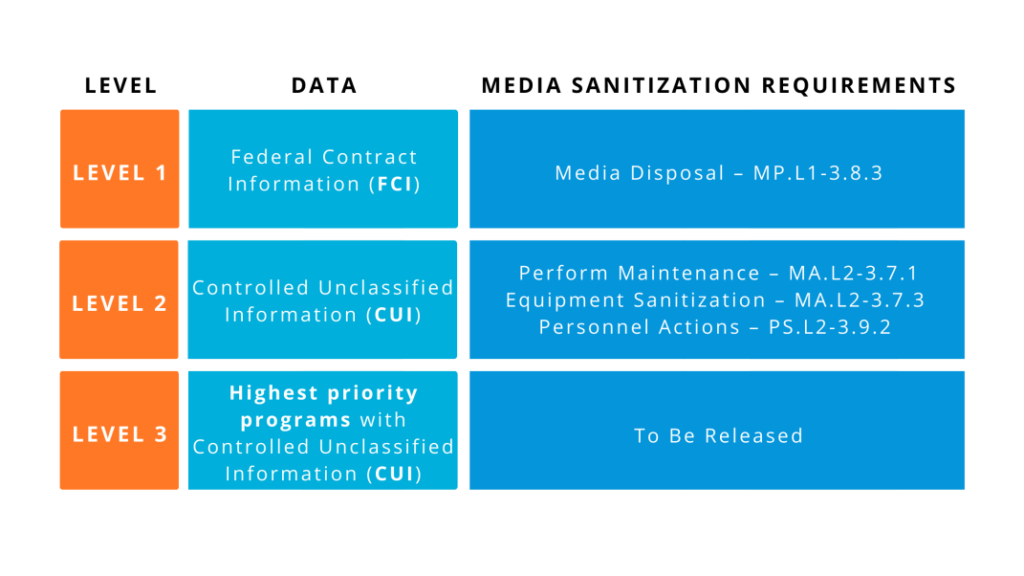
CMMC 2.0 Level 1 Media Sanitization Requirements
Out of the 17 security practices contained within the first level, we have singled out the one that’s relevant to media sanitization.
- Media Disposal – MP.L1-3.8.3
“Sanitize or destroy information system media containing Federal Contract Information before disposal or release for reuse.”
Found within the Media Protection (MP) section of CMMC 2.0, this requirement “applies to all system media, digital and non-digital, subject to disposal or reuse.” MP.L1-3.8.3 states to “clean or purge the information, if you want to reuse the device” and directs organizations towards following the NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Media Sanitization Requirements
You can find 3 security practices within the second level of CMMC 2.0 that involve media sanitization requirements.
- Perform Maintenance – MA.L2-3.7.1
“Perform maintenance on organizational systems.”
MA.L2-3.7.1 is a Level 2 Maintenance (MA) practice. In order to perform maintenance on organizational systems, contractors may have to securely destroy data from all relevant media devices and system components. - Equipment Sanitization – MA.L2-3.7.3
“Ensure equipment removed for off-site maintenance is sanitized of any CUI.”
This Maintenance (MA) practice requires contractors to sanitize equipment removed for off-site maintenance of any controlled unclassified information (CUI). MA.L2-3.7.3 can be followed by implementing the NIST SP 800-88 guidelines for media sanitization. - Personnel Actions – PS.L2-3.9.2
“Ensure that organizational systems containing CUI are protected during and after personnel actions such as terminations and transfers.”
PS.L2-3.9.2 states that contractors should protect data when closing system accounts for departing or transferring personnel. Secure media sanitization software should be used in order to permanently remove employee information before the media in question is reallocated to somebody else.
CMMC 2.0 level also includes the following security practice related to the protection of digital and non-digital media.
- Media Protection – MP.L2-3.8.1
“Protect (i.e., physically control and securely store) system media containing CUI, both paper and digital.”
A Level 2 Media Protection (MP) practice, MP.L2-3.8.1 requires organizations to protect digital and non-digital media that contains CUI. Contractors are advised to consult NIST SP 800-111 to receive guidance on using secure encryption technologies for end user devices.
CMMC 2.0 Level 3 Media Sanitization Requirements
Information on Level 3 CMMC practices and requirements is not yet available. Please consult the official website of the U.S. DoD Chief Information Officer in order to find the latest updates.
How to Prepare for CMMC 2.0
For organizations wishing to secure a contract with the DoD, it’s necessary to prove your ability to securely sanitize media that’s used to store or process sensitive information. Sanitizing FCI is enough to pass CMMC Level 1 requirements, while sanitizing CUI is needed to meet the requirements of Levels 2 and 3. If you want more information on how to securely sanitize media, keep in mind that NIST 800-88 is the reference standard for the DoD and U.S. federal government as a whole.
To help your organization with its media sanitization efforts, Jetico offers 2 trusted data wiping tools that comply with NIST’s Clear and Purge techniques:
- BCWipe Total WipeOut securely wipes entire hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs, including NVMe) beyond forensic recovery.
- BCWipe securely wipes individual files and folders from traditional hard drives and SSDs beyond forensic recovery.
Your organization may also need to demonstrate its capabilities in protecting digital media that contains FCI or CUI. For further assistance with CMMC 2.0 compliance, Jetico offers 2 encryption solutions for protecting data at rest that are fully compliant with NIST SP 800-111 requirements:
- BestCrypt Volume Encryption to encrypt entire hard drives.
- BestCrypt Container Encryption to encrypt individual files and folders.
To add some protection to potentially vulnerable data in use, Jetico’s BestCrypt Data Shelter is a free tool that organizations can use to protect selected folders from unwanted programs and users.
Want to get started with Jetico’s endpoint data protection solutions? Begin your free trial of BCWipe or BestCrypt today!
Related Articles
Data Sanitization 5 Common Myths
Hardware Decommissioning Process: A 5-Step Checklist
DoD 5220.22-M Explained – Data Erasure Standards
NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization Explained
IEEE 2883-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage
IRS Publication 4812 & How to Comply with Wiping Standards
How to Securely Wipe Your Windows 11 Computer Clean
The Ultimate Guide to Deleting Files Permanently
How to Delete Files on SSD
How to Obtain a Certificate of Destruction
