
The IEEE 2883-2022 standard was issued by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers in August 2022. Providing guidelines for sanitizing logical and physical storage, as well as technology-specific requirements for eliminating recorded data, the IEEE 2882-2022 aims to counter emerging challenges to data storage brought about by new technology.
In this blog, you can find an overview of IEEE 2883-2022 and why it’s important to your organization. You will also learn about the data erasure methods and techniques outlined in the standard, as well as the importance of verifying your sanitization results.
IEEE 2883-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage in a Nutshell
- When?
The IEEE 2883-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage was approved by the IEEE board in June 2022 and officially released in August 2022. - What?
The IEEE 2883-2022 standard provides organizations with guidance on how to effectively sanitize data on storage technology. In section 5.1, the standard explains when data sanitization should be viewed as an essential practice: “When storage devices are transferred, become obsolete, are no longer usable, or required by an ICT system, it is important that residual magnetic, optical, electrical, or other representation of data are not recoverable.”
Similar in style to the NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization, the IEEE standard replaces outdated data erasure techniques with solutions that are suitable for modern technology. - Who?
The IEEE 2883-2022 standard can be followed by any private company, organization or individual that needs to securely erase data from storage systems. While it’s not legally required to follow the IEEE standard, it’s advisable for organizations with modern devices to do so in order to ensure their sensitive data is unrecoverable.
What Is Media Sanitization?
Media sanitization is the process of erasing information from a storage device in a way that ensures it cannot be retrieved by third parties. After effectively sanitizing a device, the removed data should be unrecoverable even with the use of advanced forensic tools. In addition to removing the files and folders from your storage device, the sanitization process will securely remove all Data Remanence.
Why Is the IEEE 2883-2022 Useful to My Organization?
Despite the latest revision coming in 2014, the most commonly used data erasure standard today is still the NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization. The changes that have come about to data storage technology in the last 10 years, however, require updated standards to account for devices that are now commonly used in the workplace and at home. That’s precisely what the IEEE 2882-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage does, with the publication offering guidance on how to sanitize NVMe, SATA, SCSI and other types of modern drives.
Sanitization Methods & Techniques Outlined in IEEE 2883-2022
The IEEE 2883-2022 Standard for Sanitizing Storage describes 3 methods that can be used for erasing physical storage: Clear, Purge and Destroy.
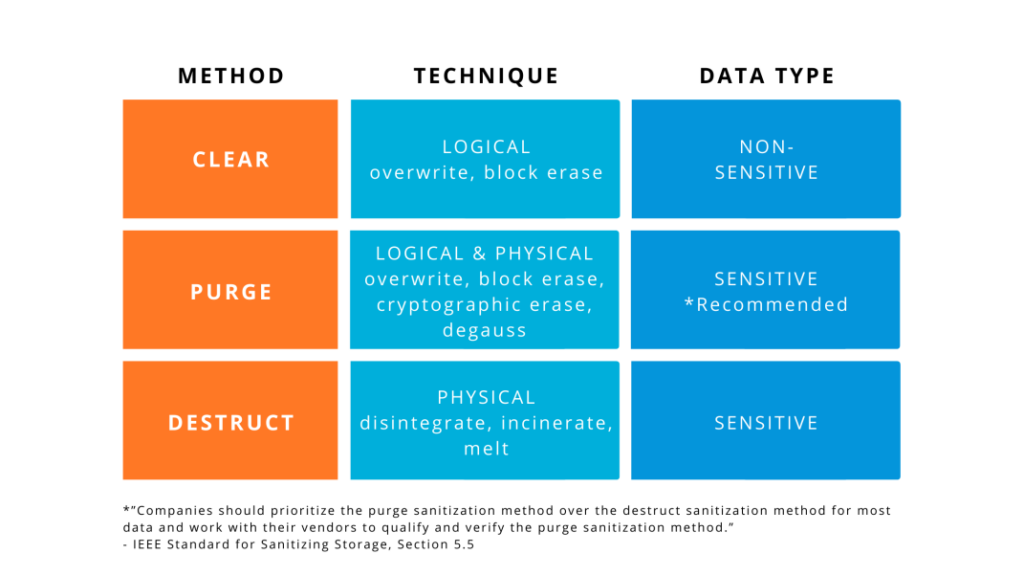
- Clear
The Clear sanitization method uses logical techniques, i.e. overwriting or block erasing, on all addressable storage locations to protect against simple, noninvasive data recovery attempts.
Clear sanitization doesn’t remove data from non-addressable storage locations, so this technique should not be used to erase sensitive information. The IEEE 2882-2022 explains that Clear techniques are to be used for low-security information, which is defined as follows: “Information if disclosed to an unauthorized party would cause mild impacts to the organization.” - Purge
The Purge sanitization method uses logical and physical techniques, such as overwriting, block erasing, cryptographic erasing or degaussing. Both addressable and non-addressable locations are targeted with this method, making the recovery of target data infeasible even when using state-of-the-art laboratory techniques to attempt data recovery.
The IEEE standard states that Purge techniques are to be used for medium-security information, which is defined as follows: “Information if disclosed to an unauthorized party would cause moderate impacts to the organization.” - Destruct
The Destruct sanitization method uses physical techniques to destroy media, resulting in target data being unrecoverable with state-of-the-art laboratory techniques and the storage media device being unusable. Physical techniques used to destroy media include disintegrating, incinerating and melting. It’s important to note that incineration requires storage devices to be burned until “reduced to ashes”, and melting requires storage devices to be liquefied.
The IEEE standard states that Destruct techniques are to be used for high-security information, which is defined as follows: “Information if disclosed to an unauthorized party would cause severe impacts to the organization.”
Section 5.5 of the IEEE standard, titled Sustainability and media sanitization, states: “Companies should prioritize the purge sanitization method over the destruct sanitization method for most data and work with their vendors to qualify and verify the purge sanitization method.” It’s also worth noting that using physical techniques to destroy media results in the creation of harmful electronic waste and rules out the possibility of devices being reused or donated. Find out more about the benefits of using data erasure and repurposing your devices.
Don’t Forget to Verify
After using one of the above sanitization methods to remove data from your device, you should finalize the process by verifying your results. Verification is an important step that checks all data has been removed, therefore delivering extra confidentiality.
Depending on the sanitization technique used, the verification process will differ:
- Clear
Verification using representative sampling should be performed. This is done by selecting random locations on the storage media that represent at least 5% of the addressable space. - Purge
Full verification of the addressable storage media should be performed. However, if cryptographic erase was used to perform sanitization, it’s potentially not possible to verify. - Destruct
A physical inspection is the only option here as storage media has been destroyed.
Prepare for IEEE 2883-2022 with BCWipe Total WipeOut
BCWipe Total WipeOut is a long-trusted data wiping solution that securely erases hard drives beyond forensic recovery. If you plan on following the IEEE 2883-2022 standard to purge data, BCWipe Total WipeOut simplifies the process by allowing you to add a verification step to the end of sanitization operations by doing nothing more than ticking a checkbox.
Get started with Jetico’s secure data sanitization solution by signing up for your free trial of BCWipe Total WipeOut or contacting out data protection specialist for a free consultation.
Related Articles
Data Sanitization 5 Common Myths
Hardware Decommissioning Process: A 5-Step Checklist
NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization Explained
DoD 5220.22-M Explained – Data Erasure Standards
CMMC 2.0 Levels, Controls & Framework for Media Sanitization Requirements
How to Securely Wipe Your Windows 11 Computer Clean
How to Wipe an NVMe Drive
How to Obtain a Certificate of Destruction
