The Ultimate Guide to Authentication Methods

Which of the following is the safest authentication method: single-factor authentication (SFA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA)? MFA also comes in several forms, but some alternatives are better than others. So, which option should you go for?
In this blog, we will examine the pros and cons of both authentication methods and discuss the most common authenticators available for MFA. Finally, we will try to help you identify which one is the safest and most user-friendly. Click here to jump to our final recommendations.
Single-Factor Authentication (SFA) vs. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
When we talk about authentication methods, we’re referring to the process of securing data confidentiality by requiring certain types of credentials. Generally speaking, there are 2 types of methods:
- Single-Factor Authentication (SFA)
SFA is the simplest form of authentication method, as it only requires users to provide one kind of credential to verify who they are. The most common example of SFA is matching a password to a username.
👍 Pros: More user-friendly. By successfully entering one type of credential, you immediately gain access to the data stored on the network, website or system in question.
👎 Cons: Passwords can be breached. If you’re using SFA, it’s very likely you will be required to enter a password. Unfortunately, even the strongest passwords aren’t immune from being leaked or cracked by cybercriminals. Without an additional factor being needed to confirm your identity, this can lead to malicious users gaining access to your data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is an authentication method that asks users to provide multiple types of credentials to confirm their identity. MFA usually works by requiring a combination of something you know (like a password) and something you have (like a USB device or token). The most common type of MFA is 2-Factor Authentication (2FA), which requires 2 separate types of credentials.
👍 Pros: Safer – 2 verifiers are better than 1. By using 2 or more separate authenticators, you can greatly limit the chances of anyone gaining access to your data.
👎 Cons: Less user-friendly. By adding an extra layer, accessing your data might become more painful and time-consuming – for example, entering an additional security code. In some cases, you also need to purchase extra hardware to successfully verify your identity, such as a token or smart card.
Which Authenticators are Available for MFA?
MFA can be performed by using several different authenticators. Here, we will list the typical ones:
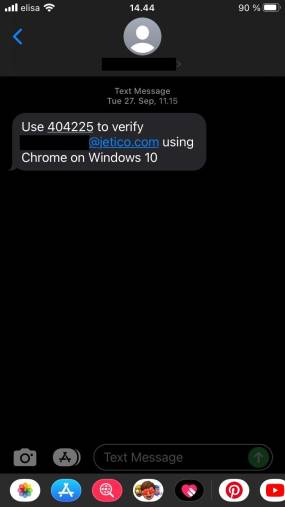
- SMS security codes
Receiving a security code via a text message is the most common way to verify your identity when using MFA. This type of authenticator generally involves a verification code that expires soon after it’s received.
👍 Pros: Convenient and easy to adopt. Messages are usually delivered to mobile devices instantly, which makes this a very convenient authentication method.
👎 Cons: SMS communications are not secure. Cybercriminals can easily intercept text messages. Using an SMS authenticator also requires you to share your phone number, which may not always be preferable.
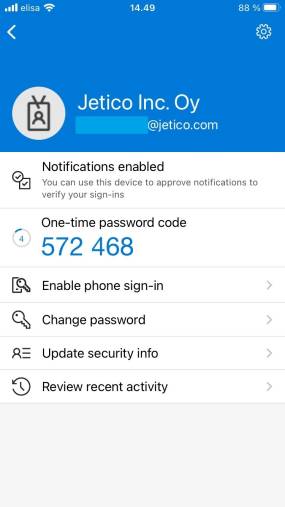
- Authenticator applications
Authentication apps, such as Microsoft Authenticator, work by constantly generating 6- or 8-digit codes. When it comes time to verify your identity, you simply log into your application and receive the code needed to gain access to the system in question.
👍 Pros: Accessible and quick to use. Most importantly, codes can’t be intercepted like they can with SMS messages.
👎 Cons: Security vulnerabilities. Some of these applications, such as Google Authenticator, are accessible without having to enter a password. This lack of security makes it possible for malware to steal MFA codes from your mobile device. Also, if your phone runs out of battery, you won’t be able to see your codes (this is also true for SMS security codes).
- USB devices
Regular USB devices can be used as a method of authentication. All you have to do is plug the removable drive into your computer’s USB port.
👍 Pros: A true physical factor people are familiar with. By being physically detached, USBs are more difficult to be intercepted by malware. Most people own USBs and everyone knows how to use them, which makes this option very accessible.
👎 Cons: Not tamper-proof. Unlike tokens, regular USBs are not tamper-proof. In addition, they are not supported by all software and systems. But if you want to use this method of authentication for your encryption, USB devices are compatible with BestCrypt Volume Encryption.

- Trusted Platform Module
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized chip located on a computer’s motherboard or in its processor. Designed as a form of tamper-proof storage to secure cryptographic keys, TPMs can be used as an additional factor when verifying your identity.
👍 Pros: Tamper-proof. Due to multiple physical security mechanisms, TPMs are tamper-proof and their security functions cannot be interfered with by malware.
👎 Cons: Not detachable. TPMs are fixed to your computer, so this option doesn’t provide the same level of security as a physically separate second factor that can be stored independently from the device you’re trying to protect. There are also some concerns over user behavior being recorded in proprietary databases.
- U2F keys (tokens & smart cards)
Universal 2nd factor (U2F) is a type of authentication method that’s used with tokens and smart cards. Authenticating is simple with U2F keys, as you simply have to plug in, tap or swipe your device of choice in order to verify your identity.
👍 Pros: The highest level of security. Like trusted platform modules, U2F keys provide a tamper-proof authentication method and a high level of security. Unlike TPMs, they are not attached to your computer, so users just have to make sure keys are kept physically secure.
👎 Cons: Additional investment. U2F keys generally have to be purchased separately, so a one-off payment is required in order to use this authentication method. Depending on which type of USB port your device has, you will also be limited to using a complementary U2F key.

So, What is the Safest Authentication Method?
Let’s go back to our initial question:
Which of the following is the safest authentication method: single-factor authentication (SFA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA)?
When it comes to the most secure authentication method, it’s clear that MFA comes out on top, especially when you’re using a token or smart card.
In the current debate surrounding authentication methods, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) says that using SFA is “exceptionally risky” and recommends all organizations to refrain from using it to avoid unnecessary risks of having their systems compromised. Practically speaking, however, some of you may decide to compromise a little on security to find a solution that suits your particular needs.
Here are our general recommendations:
- If you decide to use SFA, then you should consider reviewing and taking tangible steps to improve the strength of your passwords. Certain types of software, such as BestCrypt Volume Encryption, offer key stretching techniques to give users advanced protection against brute-force attacks. Even better, you can replace passwords altogether by authenticating with a physical device, such as a USB device that can’t be brute forced.

- If you want to go with a more user-friendly version of MFA, you could minimize the effort of authenticating by using single sign-on. Another feature included in BestCrypt Volume Encryption, single sign-on allows users to save time by automatically logging in to Windows with your encryption password.
- If you want to go with the highest level of MFA security and keep it affordable, then you should consider using a YubiKey. YubiKeys are widely available on the market and reasonably priced. Review how to implement this type of token with BestCrypt Volume Encryption.
